Wafer vacuum suction cups are usually composed of a hard surface with many small holes or channels on the surface. Through these small holes, the suction cup can be connected to the vacuum pump, resulting in a vacuum effect. When the wafer is placed on the suction cup, the vacuum pump is turned on to extract air through small holes, creating a vacuum between the wafer and the suction cup. This vacuum effect generates sufficient suction to firmly adhere the wafer to the surface of the suction cup.
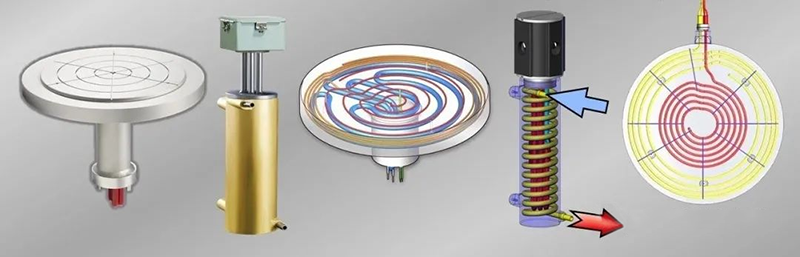
Wafer vacuum suction cups are usually circular and slightly larger than the size of the wafer. The common size range is from 50mm to 300mm in diameter, and most vacuum suction cups use a concentric ring vacuum design. Vacuum suction cups are usually matched with the standard size of wafers, and different sizes of wafers correspond to corresponding size suction cups, which cannot be mixed. For example, a 150mm (6 inch) suction cup can fix a 150mm wafer, and to be compatible with a 4inch wafer, a fixture may need to be installed.
The materials of vacuum suction cups generally include composite materials such as aluminum, brass/bronze, ceramics, and silicon carbide. Aluminum suction cups are made of aluminum, which is a relatively soft, lightweight, non magnetic, and corrosion-resistant material. Use aluminum chucks to avoid damaging the workpiece. Aluminum and aluminum alloys have excellent thermal conductivity and conductivity.
Brass/Bronze - The suction cup is made of brass or bronze or lined with brass or bronze. Brass and bronze chucks can avoid workpiece damage while still providing appropriate rigidity and precise fixation and positioning. Copper and some copper alloys have excellent thermal conductivity and conductivity, and can quickly conduct heat in cooling or heating applications. Brass is not suitable for wafer chucks in high vacuum and high temperature chamber environments because zinc in brass alloys evaporates easily.
Ceramics - Ceramic surfaces are typically used for applications that require high purity and chemical stability. Ceramics are materials produced by high-temperature fusion of minerals. Generally speaking, ceramics are electrical insulators or semiconductors and have high resistance to thermal breakdown, erosion, and damage.
There are two main types of vacuum suction cups: non hot chuck and hot chuck. Non hot cards operate at room temperature without heating or cooling function. The heat card has an overall heating or cooling function, which can maintain the wafer at a specific temperature during the processing.
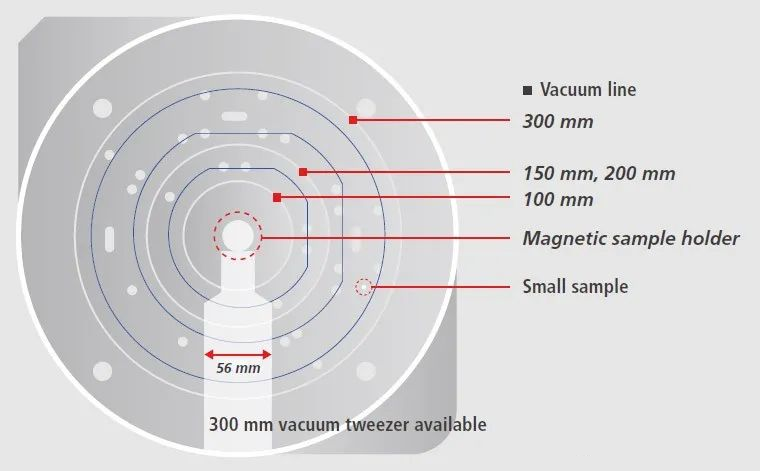
The important specifications of vacuum suction cups include outer diameter, flatness, temperature range, thermal stability, thermal uniformity, and capacitance.
Outer diameter - The outer diameter or width determines the size of the wafer that can be fixed.
Flatness - The flatness of wafer suction cups is an important indicator, usually measured in micrometers. For extreme ultraviolet lithography, a wafer chuck with high flatness is required for focusing.
Temperature range - For a hot suction cup, this indicates the temperature control range that the hot suction cup can provide. For non hot suction cups, the temperature range represents the maximum temperature at which the suction cup can operate without damage.
Thermal stability - Thermal stability represents the temperature control level of the hot wafer suction cup.
Thermal uniformity - the uniformity of temperature control over the entire wafer surface. A hot card with high thermal uniformity will not have hot or cold spots.
Capacitance - The capacitance of a wafer chuck is an important parameter of the chuck used in electrical testing or detection. Low capacitance is more suitable for testing or detection.

The characteristics of the TC200 series of high and low temperature chucks independently developed by Zhongleng are as follows:
Extended temperature range from -65 º C to+200 º C, low noise, DC control system.
Up to 5 temperature and ramp/soak/cycle thermal cycling devices can be set on the front panel.
• LAN, RS232; Optional: GPIB
No liquid nitrogen or any other consumable refrigerant is required
Efficient cooling system for reliable, low-temperature testing of hybrid vehicles and other high-power equipment
High and low temperature chuck:
The temperature controlled vacuum chuck can accommodate 300mm wafers
High precision, good temperature control, and uniform stability
Can provide standard, high isolation, and protective configurations
The advanced chuck design provides low stray capacitance and high grounding resistance, and the DC power supply can minimize electrical noise
It can interface with manual or automatic detection stations, laser cutters, or inspection stations.
Part of the content of this article is reprinted from chip manufacturing. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it. Thank you!


















