The raw materials and by-products of the pan semiconductor process contain various hazardous gases, which pose a risk of corroding pipelines. Some may encounter other hazardous substances or accumulate a large concentration, posing a risk of fire and explosion. To avoid these hazards, semiconductor factories, panel factories, photovoltaic factories, and other industries involving special gases currently install Local Scrubbers near the machine to handle hazardous gases.
Currently, there are more than a dozen brands of Scrubbers used in the pan semiconductor industry, and according to their principles, they can be roughly divided into: electric heating water washing type, combustion water washing type
Water washing type, dry adsorption type, plasma water washing type, plasma thermal decomposition dry adsorption type, catalytic adsorption type, electric heating filtration type, etc. Each type of Local Scrubber has its own advantages and disadvantages. We should choose a suitable waste gas treatment device based on the actual type and physicochemical properties of waste gas, and generally consider the following key points: cost budget, operation and maintenance cost, PM frequency and difficulty, safety and treatment efficiency What factory facilities are available on site.
There is no clear inspection measure for the validation of the treatment efficiency of Local Scrubber. Generally, as long as the volume concentration of the treated exhaust gas meets the TLV value or emission allowable concentration specified by regulations, it is sufficient;
In summary, the main function of waste gas treatment devices is to treat and purify the generated waste gas, in order to reduce negative impacts on the environment and human health. These devices are usually used in industrial production, semiconductor factories, photovoltaic plants, and other waste gas treatment facilities to treat and reduce the emissions of harmful gases and pollutants generated. The goal of these exhaust gas treatment devices is to reduce the concentration of harmful substances in the exhaust gas, ensure that emissions comply with environmental regulations and standards, and protect the environment and human health.
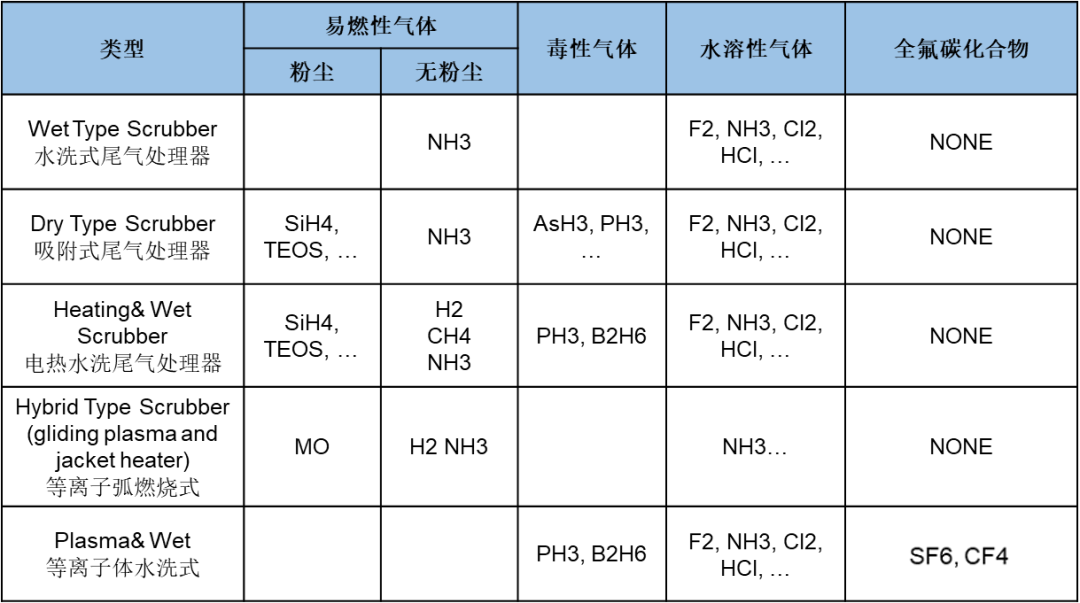
Classified by product type:
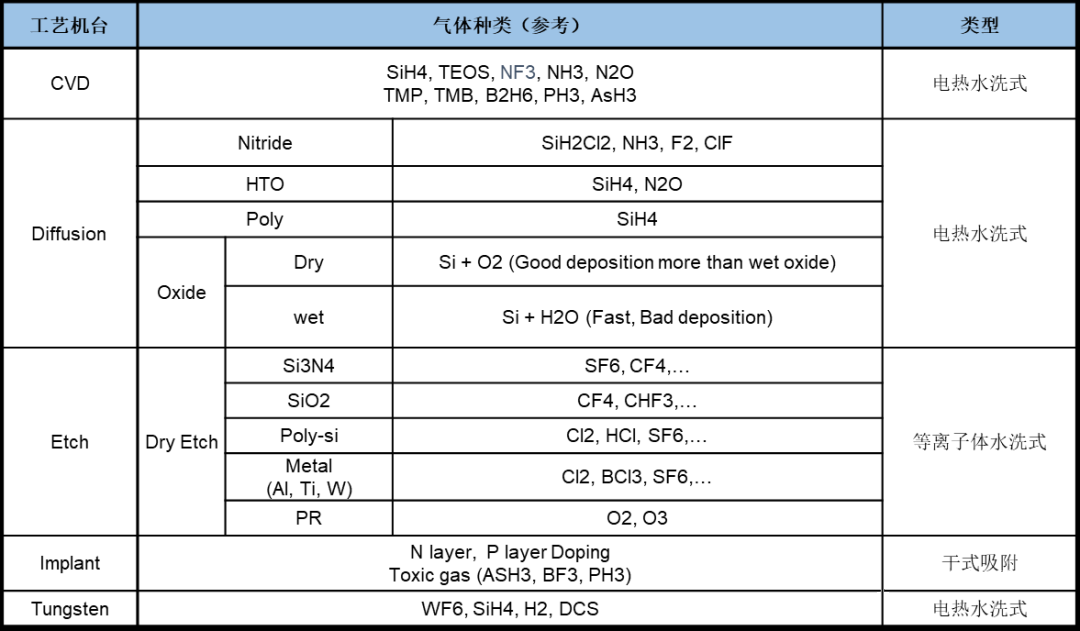
Divided by process machine:
Introduction to commonly used exhaust gas processors:
|
Types |
Application |
Processing |
|
Plasma water washing type |
1. Combustible and corrosive gases (SiH4, SiH2CL2, TEOS, H2, NH3, CL2, F2, HCL, NH3, PH3, BCL3, etc.) 2. Thoroughly decompose PFCs gas (SF6, CF4, NF3,) through Plasma 3. Process water-soluble gases after decomposition of PFCs; 4. Maximum intake capacity 600slpm; |
Etch |
|
Washed |
1. Process water-soluble gases (NH3, CL2, HF, F2, HCL, etc.); 2. The maximum processing capacity is 600slpm (including GN2); |
Etch |
|
Dry adsorption type |
1. Treat toxic gases (BCL3, HCL, CL2, HF, HBr, F2, CLF3, NH3, PH3, AsH3, TMAl, SiH4) through chemical adsorption; 2. Adsorbent capacity: 100L; 3. It is prohibited to use the same adsorbent for incompatible gases; AsH3 intake ≤ 2slpm, PH3 intake ≤ 2slpm; |
Implant, LED AlGaInP InP GaAs MOCVD, HVPE |
|
Electric hot water washing type |
1. Handling flammable gases/water-soluble gases/flammable toxic gases (SiH4/SiH2CL3, TEOS, H2, NH3, CH4, CL2, F2, HCL, NH3, PH3, BCL3, NF3) 2. Handle certain flammable toxic gases. 3. Unable to process PFCs (perfluorocarbons) (with an efficiency of 80% except for NF3), but able to process gases after PFCs dissociation, such as PFCs dissociation into F2 and HF 4. The maximum processing capacity is 600slpm (including GN2 CDA); |
CVD(PECVD, LPCVD, APCVD, SACVD, MOCVD, ALD) |
This article is reprinted from the internet. If there is any infringement, please contact to delete it. Thank you!


















