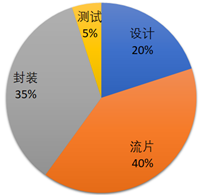
There are several important links from chip design to finished product, namely, design ->chip ->package ->test. However, the proportion of chip cost composition is quite different, generally 20% of the labor cost, 40% of the chip cost, 35% of the package cost, and 5% of the test cost [For advanced processes, the chip cost may exceed 60%]. Testing is the cheapest step in all aspects of the chip, but testing is the last step of product quality. If there is no good testing, the PPM [million failure rate] of the product is too high, and the return or compensation is far beyond the 5% cost.
What tests does the chip need to do?
It is mainly divided into three categories: chip function test, performance test and reliability test. Three tests are indispensable for chip products to be launched.
Function test, to see if the chip is correct, is to test the parameters, indicators and functions of the chip to see if it can reach the design function.
The performance test depends on whether the chip is good or not. Because there are countless possible steps to introduce defects in the manufacturing process of the chip, even if the same batch of wafers and packaged products are good or bad, the chip needs to be screened to discard the bad chips.
In the reliability test, whether the chip is firm or not, the chip has passed the function and performance test and got a good chip, but whether the chip can work normally in various working environments, and whether the chip can be used for one month, one year, or ten years, all of these should be evaluated through the reliability test.
What testing methods do we have to implement these tests?
Test methods: board level test, wafer CP test, packaged finished product FT test, system level SLT test, reliability test, and multiple strategies.
Board level testing is mainly used for functional testing. It uses PCB+chip to build a "analog" chip working environment, leads out all the interfaces of the chip, checks the function of the chip, or checks whether the chip can work normally in various harsh environments.
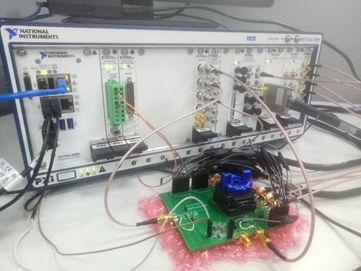
Wafer CP test is often used in function test and performance test to find out whether the chip functions normally and screen out the faulty chips in the chip wafer. CP [Chip Probing], as its name implies, uses a probe [Probe] to pierce the chip on Wafer, input various signals into the chip, grab the chip output response, compare and calculate it, and some special scenarios will be used to configure and adjust the chip [Trim].
FT test of finished products after packaging is often used in function test, performance test and reliability test to check whether the chip functions normally and whether there are defects in the packaging process, and to help detect whether the chip can work after "fire, snow, thunder and lightning" in the reliability test.
System level SLT testing is often used in functional testing, performance testing and reliability testing. It often exists as a supplement to FT testing of finished products. As the name implies, it is to test a chip in a system environment by running its functions in its normal working environment. The disadvantage is that it can only cover part of the functions and has low coverage, so it is generally a supplement to FT.
Reliability testing is mainly to apply various harsh environments to the chip, such as ESD static electricity, which is to simulate human body or industrial body to apply instantaneous high voltage to the chip. Another example is aging HTOL [High Temperature Operating Life], which is to accelerate chip aging under high temperature and then estimate chip life. In addition, HAST [Highly Accelerated Stress Test] tests the humidity resistance of the chip package. The product to be tested is tested under severe temperature, humidity and pressure. Whether the moisture will penetrate into the package along the gel or the interface between the gel and the wire rack, thus damaging the chip.
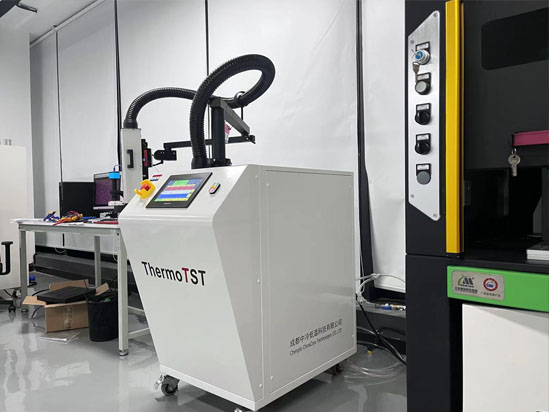
The high and low temperature impact equipment TS-760 of Chengdu Intercooling&Low Temperature Co., Ltd. provides reliability tests such as aging test, characteristic analysis, high and low temperature temperature change test, temperature impact test, failure analysis, etc., for the cold and hot test of electronic components/modules such as chips, microelectronic devices, integrated circuits (SOC, FPGA, PLD, MCU, ADC/DAC, DSP, etc.), flash memory Flash, UFS, eMMC, PCBs, MCMs, MEMS, IGBT, sensors, small module components, etc. Temperature conversion from - 55 ℃ to+125 ℃ for about 10 seconds; Through long-term multi working condition verification, it meets the requirements of various production environments and engineering environments.

Chip testing is not only "picky" and "strict", but also requires full process control and participation. From chip design, chip startup verification, chip streaming to mass production stage testing, each stage needs to solve the corresponding demands, and solve the problems of how to continuously optimize the process, improve program efficiency, reduce time, and reduce costs. Testing in the mass production stage is particularly important to directly respond to customer complaints and low PPM. So chip testing is not just a matter of cost, but the key to balancing quality, efficiency and cost!


















