Chip testing -- In short, it is to check whether the chip is qualified through ATE (auto test equipment) after the completion of chip manufacturing. In the manufacturing process of chips, there are inevitably defects. We should separate pass and fail chips.
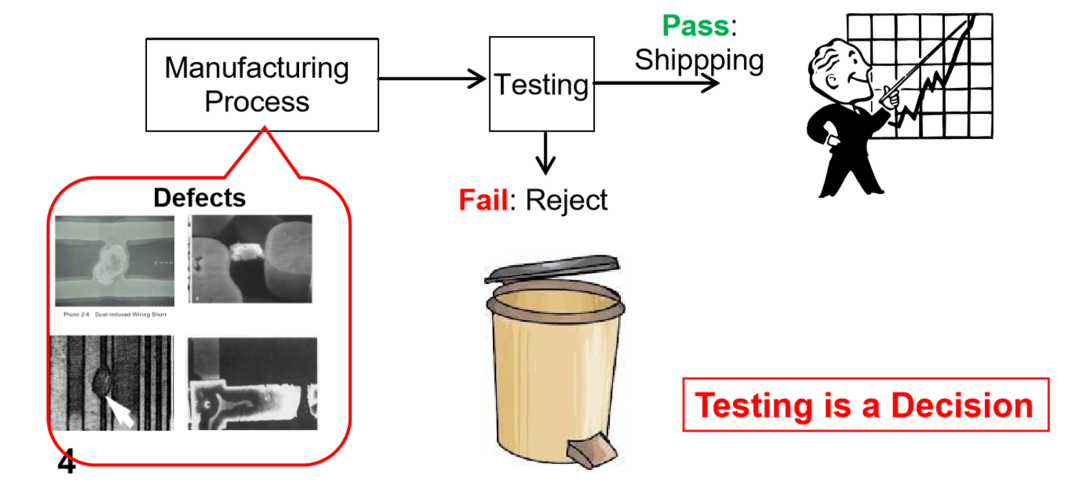
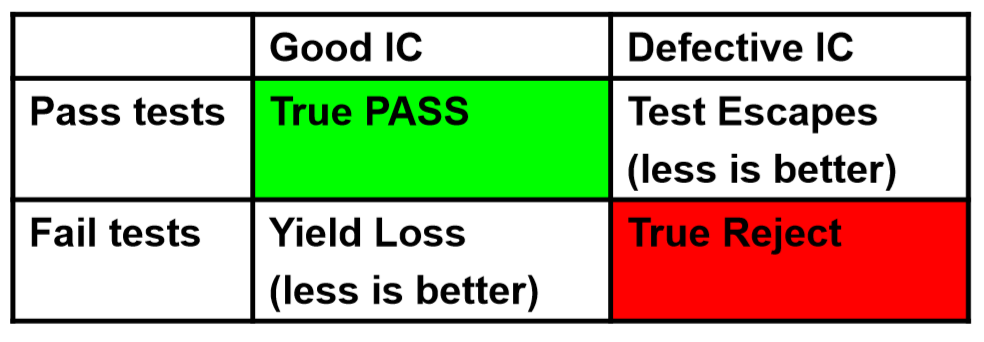
There are three results of chip test, namely:
·Good chips pass the test and remain; If the bad chip fails to pass, throw it away;
·The bad chip passed the test, which is called Test Escape;
·A good chip fails the test. The technical term is Yield Loss, also known as Over Kill;
Our goal is to minimize Test Escape and Yield Loss, but we often need to trade off between chip test cost and test quality:
·High quality testing will reduce test escape, but also increase yield loss;
·Low cost testing will reduce yield loss, but increase test escape.
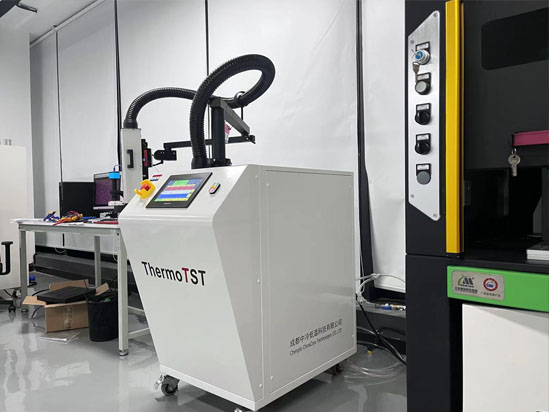
Chengdu Intercooling Cryogenics Technology provides the IC chip temperature impact tester TS-780 with high quality and cost-effective, which can accurately and quickly realize the high and low temperature cycle test, thermal stock test, aging test, reliability test, etc. of electronic components such as electronic chips.
The temperature conversion of TS-780 is from - 55 ℃ to+125 ℃ for about 10 seconds, and has a wider temperature range of - 80 ℃ to+225 ℃; Through long-term multi working condition verification, it meets the requirements of more production environment and engineering environment.

Why is chip testing so important?
That's because chip testing can ensure chip quality, shorten the time to market, and improve company profits. Chip testing plays an important role in the whole chip production process, and is in the middle of the chip design and manufacturing process. The parts of chip testing include:
Prototype test: Prototype test is generally conducted after the chip is just designed and handed over to Fab for streaming. It needs to be modified many times before the final test scheme can be determined;
Product Test: Mass production test is the test conducted after Fab's mass production, mainly including WAT, CP, FT, etc;
Diagnosis, diagnostic testing is aimed at finding root cause through a series of tests for failed chips. The ultimate goal is to improve the method to improve the yield;
Failure analysis is generally to cut the chip physically, debug the microstructure, and analyze the root cause of chip failure.
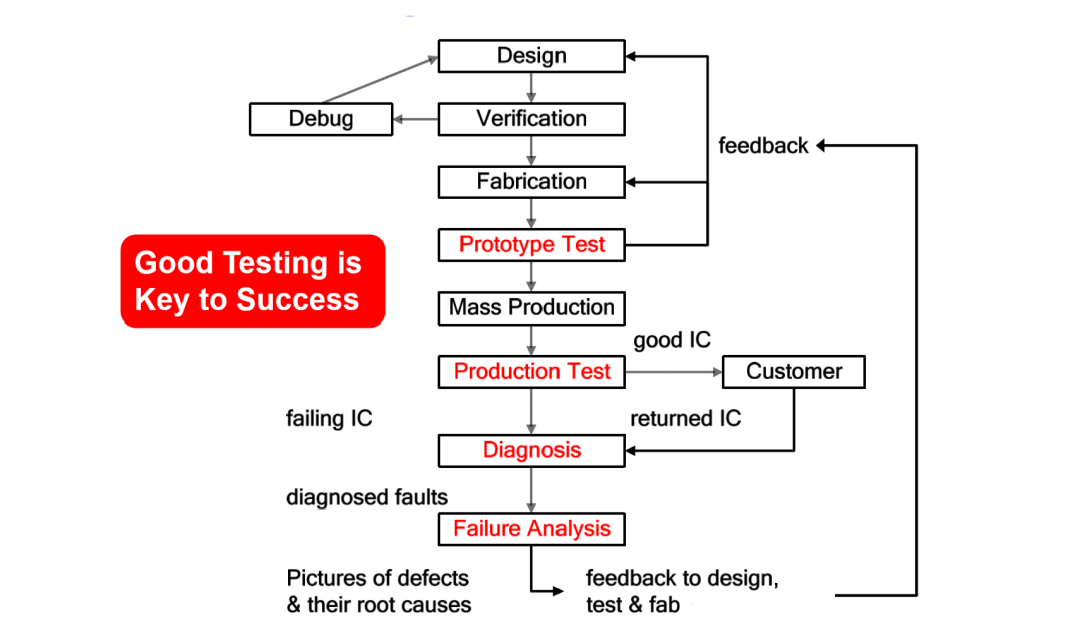
From a macro perspective, chip testing is not only the responsibility of test engineers, but also the responsibility of all chip practitioners:
Fab is responsible for ensuring the stability of the manufacturing process and improving the chip yield;
PFA is responsible for analyzing the physical structure of the failed chip;
Test Service is the maintenance of ATE machine and analysis of Test data;
The design engineer should consider the test problem in the design phase. Now there are special DFT engineers, mainly using three methods: Scan Chain, Boundary Scan, and BIST to solve the test problem;
Reliability: Reliability engineers mainly use Burn in and other methods to accelerate chip failure and simulate the life of the chip;
EDA software is mainly used to insert DFT structures, generate ATPG (auto test pattern generation) for test vectors, and fault simulation;
The test engineer is mainly responsible for writing test programs, reducing test costs and improving test quality.


















