The 400G optical module is mainly used for photoelectric conversion. The electrical signal is converted into an optical signal at the transmitting end, and then transmitted through optical fiber. At the receiving end, the optical signal is converted into an electrical signal. The transmission rate of 400G optical module is 400G, which was born to adapt to the network market of 100M, 1G, 25G, 40G to 100G, 400G, and even 1T. The 400G optical module plays a crucial role and influence in building the 400G network system.
The full name of OSFP is Octal Small Form Factor Pluggable. This standard is a new interface standard that is not compatible with existing optoelectronic interfaces. Its size is 100.4 * 22.58 * 13 mm ^ 3, slightly larger than the size of QSFP-DD, requiring a larger PCB area. The pins of the electrical interface are different from QSFP-DD, with one row at the top and bottom.

The full name of QSFP-DD is Quad Small Form Factor Pluggable Double Density. This solution is an extension of the QSFP interface, adding one line from the original 4-channel interface to 8 channels, known as dual density. This solution is compatible with QSFP solutions, which is one of its main advantages. The original QSFP28 module can still be used by simply inserting another module.
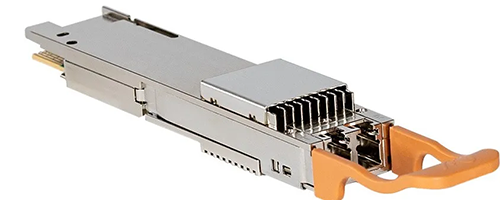
CFP8 is an extension of CFP4, increasing the number of channels to 8 and correspondingly increasing the size to 40 * 102 * 9.5 mm ^ 3. The cost of this solution is relatively high, requiring the use of 16 25G lasers.

CWDM8 is an extension of the CWDM4 standard, with a rate of 50G per wavelength, which can also reach 400G. Four new center wavelengths have been added, namely 1351/1371/1391/1411nm. The wavelength range has become wider, with higher requirements for Mux/DeMux, and the number of lasers has doubled, with a maximum input power of 8.5dBm.

The CDFP standard was born earlier, and so far, the third edition of the specification has been released. It uses 16 channels with a single channel rate of 25G. Due to the large number of channels, the size is relatively large.

COBO stands for Consortium for on Board Optics, which means placing all optical components on a PCB. The main advantages of this solution are good heat dissipation and small size. However, due to the lack of support for hot swapping, it will be difficult to repair any module that malfunctions.

The main function of the 400G optical module is to improve data throughput and maximize the bandwidth and port density of the data center. The future trend of 400G optical modules is to achieve wide gain, low noise, miniaturization, and integration, and provide high-quality optical communication modules for the next generation of wireless networks and ultra large data centers.
Nowadays, the progress in the development and mass production of 400G optical modules is relatively satisfactory. In the current market context, the demand for bandwidth in ultra large data centers is growing, and 400G optical communication modules have become the best choice to improve system performance and reduce bandwidth costs. The emergence of 5G networks will become another positive factor driving the market value of 400G optical modules.
This article is reprinted from the internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it. Thank you!


















