According to application scenarios, chips can usually be divided into four levels: consumer level, industrial level, vehicle specification level, and military level. The requirements are in order: military>vehicle specification>industrial>consumption. Car grade chips are chips used in automobiles. Unlike consumer and industrial grade chips, they require higher reliability, such as operating temperature range, working stability, defect rate, service life, and safety. Car grade chips can be understood as fully meeting the relevant certification requirements of the production process and product settings.
The market size of automotive storage chips will continue to expand, with DRAM and NAND as the demand priorities. Memory chips are widely used in intelligent vehicles and electric vehicles. The realization of system functions such as intelligent cockpit, Vehicle-to-everything, automatic driving, information entertainment, instrument panel, black box, power transmission, etc. requires storage technology to provide parameters. Autonomous driving places higher demands on the computing power and storage capacity of automotive memory chips; It also requires continuous upgrading of storage chip technology. The driving force of smart cars on storage chips mainly comes from four major fields: in car infotainment systems (IVI), advanced driving assistance systems (ADAS), in car information systems, and digital instrument panels.
Secondly, the improvement of autonomous driving level will also promote the continuous increase in the number and pixels of car cameras, corresponding to the continuous increase in car CIS. The application scenarios of automotive CIS in intelligent vehicles are very extensive, mainly divided into three categories: vision, in cabin, and forward processing of advanced driving assistance systems (ADAS). Vision includes reversing image, front view, rear view, top view, panoramic parking image, and car mirror replacement, which are used for passenger monitoring, Sleep-deprived driving monitoring, instrument panel control, dash cam (DVR), and airbag in the cabin, and for advanced driving assistance system (ADAS) forward processing, such as forward collision warning, lane departure warning, automatic high beam control, traffic signal recognition, pedestrian detection, adaptive cruise control, night vision, and so on. The expansion of the application field of automotive CIS has given rise to broad market prospects.
In addition, the demand for automotive electronic intelligent vehicle MCUs has doubled (about 70 traditional automotive MCUs, 100-200 new energy vehicles, and over 300 L2 level or above automotive MCUs), and the electronic intelligence of automobiles, the Internet of Things, and the "lack of cores" have made automotive MCUs the most promising chip segment market. With the development trend of automotive automation and electrification, the electronic and electrical architecture is being restructured, and MCU is widely used in dashboard, climate control, entertainment information, body electronics and chassis, as well as ADAS systems. The demand for MCU quantity is increasing exponentially. The market demand for on-board MCU is mainly concentrated in 8-bit, 16 bit, and 32-bit microcontrollers, with application scenarios including various subsystems of the vehicle body, power transmission system and vehicle control, instrument panel control, entertainment information system, ADAS, and safety system. The complexity of application scenarios increases as the number of MCU products increases.
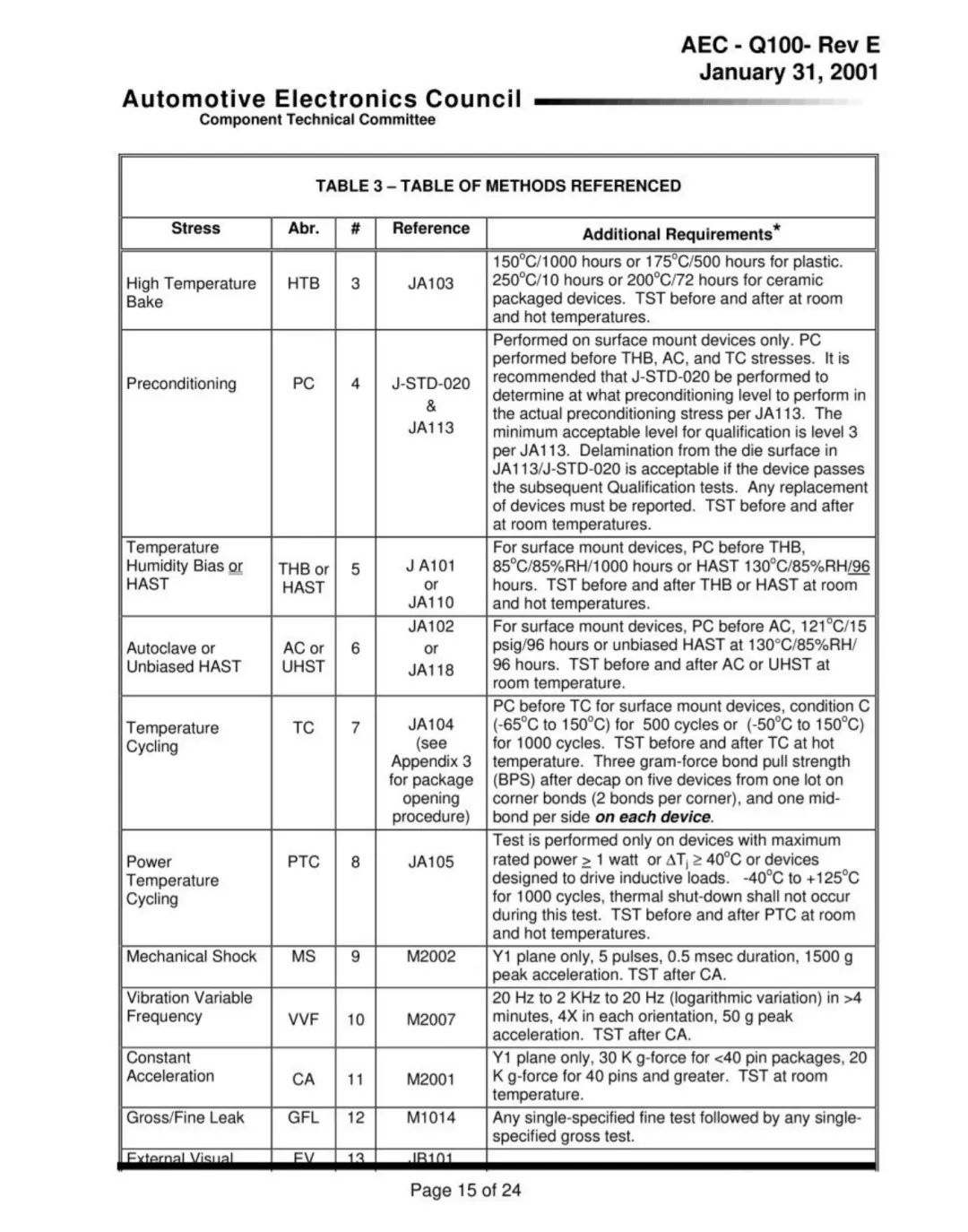
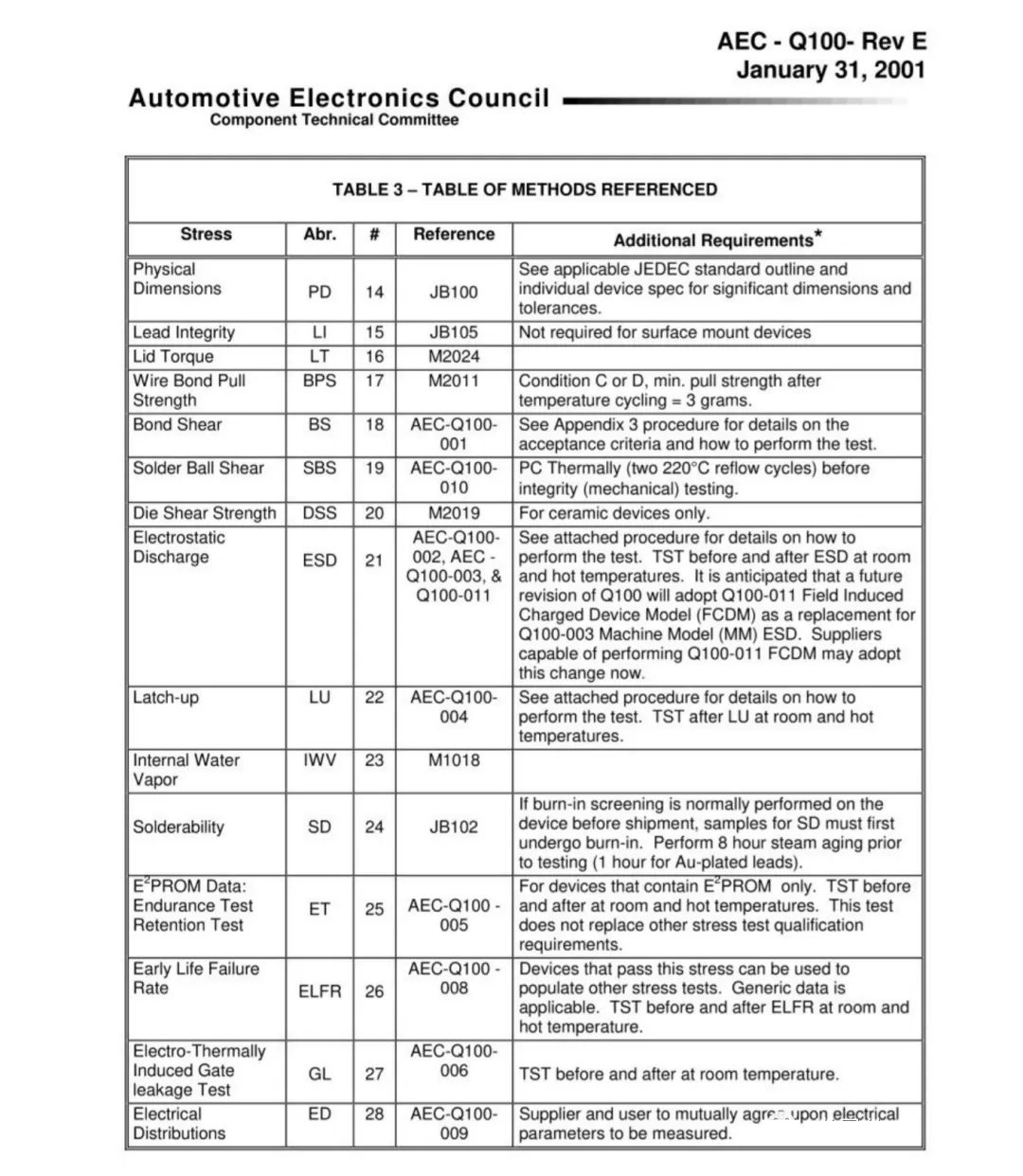
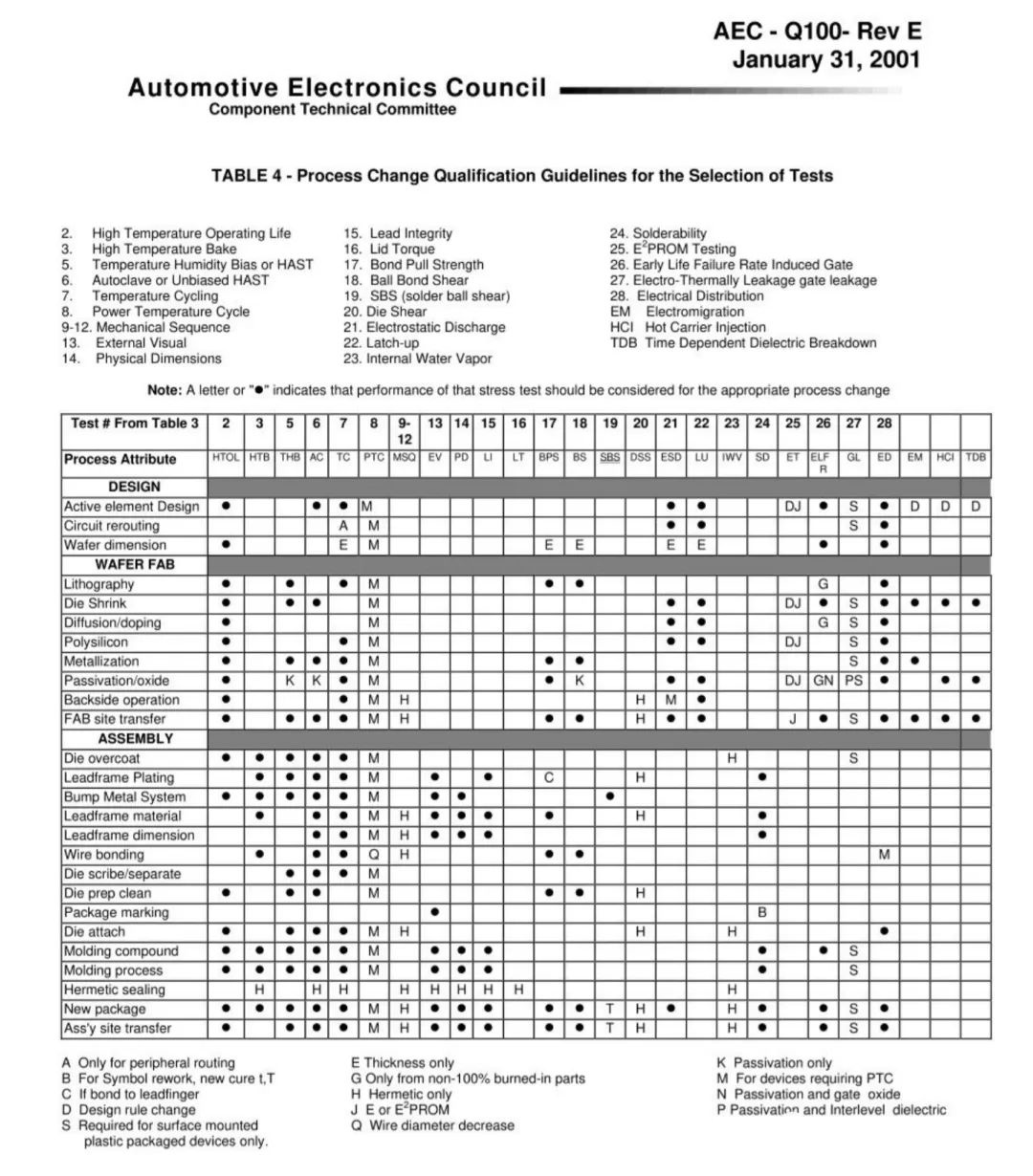
Automotive chips pass the AEC-Q100 reliability certification test conditions, requiring multiple rounds of validation and more emphasis on multi-party collaboration (cooperation between industry chain enterprises such as wafer factories and packaging factories), with a generally long cycle. Chip design manufacturers need to give high priority to reliability requirements during the product design phase to ensure that their products meet stringent requirements such as environmental stress acceleration verification, life acceleration simulation verification, and packaging verification. It is also necessary for chip manufacturers to fully and successfully manufacture car specification chips, so that they can be in place at all stages in the early stages and ensure compliance with various standards and requirements in verification.